Web Server vs Application Server
Most of the times these terms, Web Server and Application Server are used interchangeably. Let's see some of the key differences in features of Web Server and Application Server:
Web Server is designed to serve HTTP Content. Though Application Server can also serve HTTP Content, but it is not limited to just HTTP. It can be provided other protocol support as well, such as RMI/RPC.
Web Server is mostly designed to serve static content, though most modern Web Servers have plugins to support scripting languages like Perl, PHP, ASP, JSP etc. through which these servers can generate dynamic HTTP content.
Most of the Application Servers have Web Server as integral part of them, that means Application Server can do whatever Web Server is capable of. Additionally, Application Server have components and features to support Application Level Services such as Connection Pooling, Object Pooling, Transaction Support, Messaging Services etc.
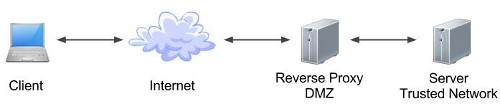
As Web Servers are well suited for static content and Application Servers for dynamic content, most of the production environments have web server acting as reverse proxy to application server. That means while servicing a page request, static contents (such as images/static HTML) are served by web server, and by using some kind of filtering technique (mostly extension of requested resource) web server identifies dynamic content request and transparently forwards it to Application Server. Example of such configuration is Apache Tomcat HTTP Server. Apache Server is Web Server and TOMCAT is a Java Servlet Container. Oracle WebLogic, WILDFLY (formerly JBOSS) are complete Application Servers.
In some cases the servers are tightly integrated such as IIS and .NET Runtime. IIS is a web server, when equipped with .NET runtime environment, IIS is capable of providing application services.